3 minute read
Semantic data layer: Why (& how) it gives meaning to your data
A semantic data layer provides a contextual view of your data to help you extract meaning from it. Here's how it can benefit you.
Table of contents
Semantic data layers allow business users to search and analyze data in a simple, effective way. With a good semantic layer, the underlying real-world narrative that raw data (e.g. databases, Word docs, website pages, etc.) offers becomes clear and easily searchable.
Ever experienced the swimming feeling in your head when you’re bombarded with information that you can’t quite extract the full meaning out of?
This is quite common in a world of one-click publishing.
Just write your post and click publish!
However, this confusion is detrimental to productivity, especially if this happens in a business environment with an internal enterprise search solution or data platform.
That’s where a semantic data layer comes into play…
Semantic data layer: What it is and why you need it
The semantic layer is what sits on top of your data, providing meaning to it.
Extracting the true value of data means knowing what you are looking at when you are examining it. Data.world explains why it is so important to cut to the true meaning of the data you are working with:
“In and of itself, data has little value. It’s the knowledge that can be gleaned from your data that’s worth its weight in gold. And that’s why it’s crucial to build a layer of knowledge — the semantic layer which consists of the key business concepts and the relationships between them about your organization. The semantic layer should live in your data catalog because that is where it’s defined, explained, and mapped to the source data.“

A semantic layer structures information into helpful categories so users can easily find specific information when searching through extensive data collection like databases full of emails or customer records stored online.
It can add value to your data lake and business by providing a structured representation of the data, and facilitating research and analysis.
Benefits of a semantic data layer
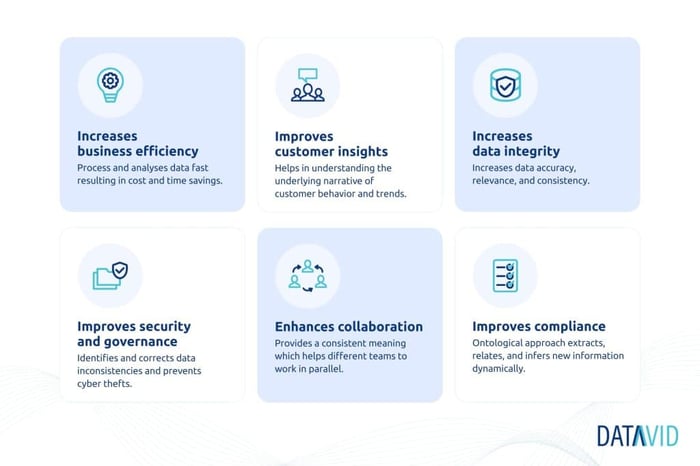
The semantic layer can provide several benefits to businesses, including:
Benefit #1: Increased business efficiency
By processing and analysing data quickly and effectively, the semantic layer reduces cost by optimising internal processes and minimising manual work.
Benefit #2: Greater insight into customer behaviour
By understanding the semantics of data, businesses better understand customer behaviour and trends to create targeted marketing campaigns and personalised customer service.
Benefit #3: Improved data integrity
It ensures data accuracy, relevancy, and consistency across different sources. This reduces the time and resources needed to manage, integrate, and analyse data.
Benefit #4: Reduction in data security risks
A semantic layer identifies and corrects any inconsistencies in data before it is used to prevent data theft.
How a semantic layer improves your data practices
A semantic layer can help organise your company’s data so that it’s easy to find, share, use, and update.
- Finding: You can find quick answers to your questions about something specific (like the name of a drug). You can filter down instantly by using filters like “upper body respiratory disease” or “respiratory disorders.” This makes it easier for users who aren’t necessarily technical experts but want answers quickly, as well subject matter experts to review technical documents.
- Sharing: It unifies data silos and enables collaboration across teams by providing data access simultaneously.
- Use: It allows everyone who has access to the system to see all its contents in one place. This makes it easier for people to find and reuse information in a cost and time-efficient manner.
- Update: It does version control by keeping track of changes. If one person updates an item, then someone else comes along and updates it in a different way or adds something new, a semantic layer will be able to show both versions so that you can see what changed and why.
Example: Better data analysis for your enterprise
The semantic layer allows you to identify and understand the relationships between data either by machine learning algorithms or human-coded rules.
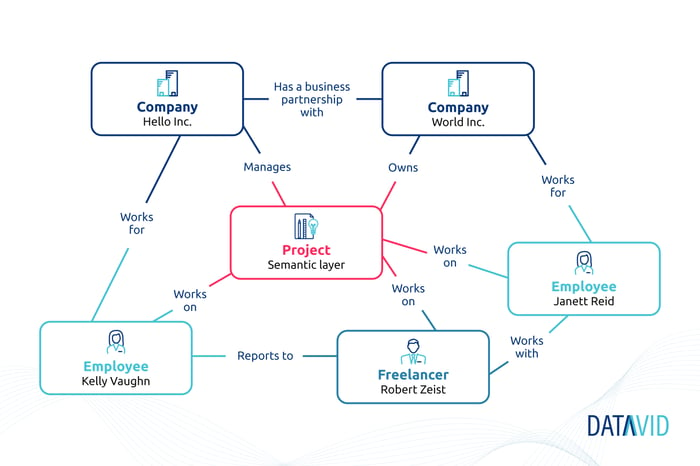
Machine learning algorithms are powerful but require large amounts of training data; if you don’t have enough, they will not work well as they cannot learn from incomplete information.
Human-coded rules allow users to define relationships between fields without having to access your data, or existing “corpuses” available on the web, like a Pharma ontology for example.
Either approach enables you to use data effectively by combining datasets to derive insights and make them available to business users - not just technical people.
Want to build your own semantic data layer?
Data sources like data lakes and data warehouses are invaluable to all businesses as they offer valuable stores that can be mined for information.
However, these data sources are of minimal value without a semantic layer that can identify the data items and relationships within them.
Implementing a semantic layer is not simple given the stakes involved and the numerous pieces that need to fit perfectly. The right solution provider can make the process seamless, cost-efficient, and effective.

With Datavid Rover, you can put all of your data to immediate use and derive maximum value out of data intelligence projects.
It brings together disparate data sources to find the right information in no time.
With a semantic layer, you will harness your data’s full potential, giving you unexpected insights and resulting in smart decisions and better business outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a semantic layer?
A semantic layer is a business representation of data from an end-user perspective.
How does the semantic layer reduce data risks?
The semantic layer enhances security by identifying and correcting any inconsistencies in data before it gets used.
How does the semantic layer improve data analysis?
The semantic layer identifies and understands the relationships between data either through machine learning algorithms or human-coded rules.




