6 minute read
What is an enterprise data management framework? [Guide]
An enterprise data management framework enhances your company's ability to develop sustainable and robust data management practices.
Table of contents
An Enterprise Data Management (EDM) framework significantly enhances your company’s ability to develop sustainable, “fluid”, and robust data management practices that support the achievement of your strategic objectives.
It’s a framework that handles your company’s data as a strategic asset and allows you to extract the maximum value from your data.
An effective EDM framework enhances the usability, regulatory compliance, and overall reliability of your data assets.
It is the mechanism that can harness reliable and high-quality data and allow your company’s leadership to make data-driven decisions and develop fact-based policies.
Why Implement a data management framework?
Your company’s data isn’t just a byproduct of doing business; it’s a marquee business asset.
As such, it should be inventoried and shared properly among your organisation if you want to maximise the value of your data…
The ability to manage ever-increasing amounts of data is widely acknowledged as a crucial component of business success, yet so many companies remain badly behind the curve.
For example, more than 70% of employees have access to data they should not.
Until you have a solid EDM framework in place that is able to integrate all this data properly, it’s hard to transform data into valuable intel that can guide, rather than mislead, key stakeholders at the company.
Companies are continuing to suffer from data breaches, data goes rogue in inaccessible silos, unreachable by the staff that needs it, and, data technologies at many companies just aren’t up to meeting the demands that are put on them.
It is the companies that are willing to acknowledge that a strong EDM framework is a strategic initiative and who are willing to invest in the framework who will be the companies that lead their industries tomorrow.
Data accountability and governance
Data flows like a river through your organisation.
Throughout its journey, it picks up new metrics along the way and becomes enhanced and/or modified with other data metrics as people from various departments work with the data.
(Sales, operations, purchasing, etc.)
The data accountability and governance framework is the mechanism that accounts for this shared ownership and accountability and its primary role is to maximise the quality of your company’s data throughout its lifecycle.
One element of governance is security, which turns out to be pretty important to your customers considering that 92% believe it’s crucial for you to safeguard their personal information.
Take steps to establish a data governance team and assign data stewards who will be accountable for the security protocols of organisational data.
Your data governance entity will be the foundational component of your EDM framework by serving as the decision-making entity that has authority over your company’s data management actions.
One note to make: data governance isn’t synonymous with data management.
If your company uses Quickbooks for accounting, that is a form of data management.
Data governance determines how the information in Quickbooks gets accessed by your employees based on the relationship they have with it.
Metadata management
Now, for the data itself. Metadata is dynamic, ever-changing “data about other data” that is generated whenever data is created, modified, read, moved, or integrated anywhere else throughout your company.
Metadata management is a set of processes that ensures the proper creation, storage, integration, and control of this data so that your company can use the data more efficiently. Metadata management benefits include:
- The ability to trace data back to its origination
- Identifying accountable parties for each of your company’s data domains
- Knowing in advance how a planned change to a data domain will impact all integrated systems
Technical and operational metadata is data that can provide developers and technical users with a clear understanding of their own technical systems such as database information.
(Column names, table properties, etc.)
There is also operational metadata that can provide IT operations with information on how data moves through their systems.
The increase in the utilisation of cloud-based services by small manufacturers has led to the creation of more siloed systems, and they can be lethal to a data-centric organisation.
Without a metadata management strategy to manage data during its lifecycle, you will likely end up contending with the adverse effect of silos and inconsistent data.
Understanding the metadata that moves through your company is crucial and it needs appropriate management.
Architecture: Data hubs, lakes, and warehouses
The ultimate purpose of your EDM framework efforts is to convert the metadata you collect into meaningful information.
Different types of data can flow into a company from a wide array of sources, in many formats and in different quantities, and the data can change as it flows through your company.
This can cause a company’s data management capabilities to be quickly consumed leading to performance degradation, such as your end users complaining about slower response times, systems freezing, etc.
When evaluating your enterprise data architecture responsible for warehousing and routing your company’s data, you need to consider:
- All types of data being stored
- Volume of data
- How much data is produced on a weekly, monthly, and annual basis
- What do you want to use the data for
Your data assets should be prioritised and key integration points should be identified that will potentially yield benefits. Interoperability should be your chief concern when adding new technology to your existing data center.
There are three common enterprise data components that will warehouse your data and make up what is referred to as a data center:
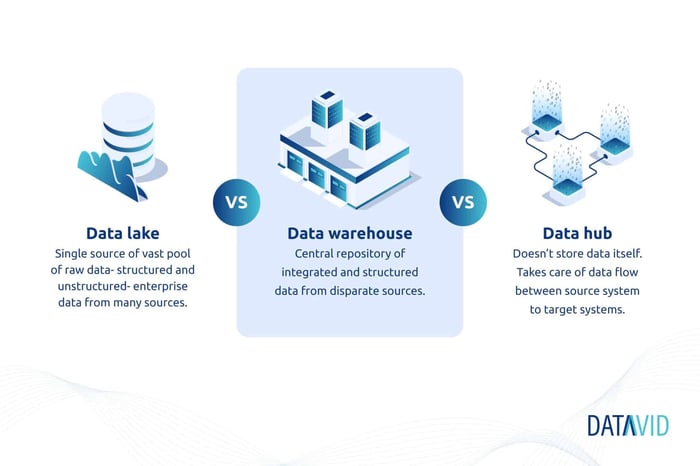
- Data Lakes: Endpoint housing structured and unstructured data used primarily for analytics, reporting, and machine learning. Raw data.
- Data Warehouses: Endpoint housing only structured data used for analytics and reporting. A powerful resource for obtaining crucial analytics.
- Data Hubs: Used primarily for operational processes, and do not serve as endpoints but rather as integration points for data sharing.
Enterprise data hubs facilitate the fluid sharing of data from across the entire landscape of your company in one, central location.
Integrating this component into your existing architecture merits a comprehensive inventory of your data assets, an understanding of the sources, and the relationship your data has to one another.
Data architecture management
Data architecture is the set of policies and results that govern and define the type of data that is collected and how the data is used and distributed throughout a company.
It provides a formal approach to creating and managing the flow of data and how the data is handled and processed across an organisation’s array of IT systems and software applications.
Your data architecture management system determines the following:
- Provides a standard business vocabulary
- Express strategic data requirements that reflect the business needs
- Outlines integrated technical designs to meet these business needs
- Ensures alignment with enterprise strategy and related business architecture
Data provisioning
We’ve established how data inevitably gets modified as it moves through the different business processes at your company; referred to as the data lifecycle.
This can present a challenge for employees who need to have the right data for their business needs.
Your company’s data provisioning effort identifies the authorised data sources for each of your key data domains and facilitates the methods to orchestrate the pull/push solutions for provisioning the data.
The flow of the data follows the following steps:
- Identifies authorised data sources
- Establishes a plan for data distribution
- Implements data provisioning tools
- Oversight of authorised data provisioning points
Data quality control
Quality control establishes the structure that your company needs to have in order for it to have the right data to fulfil the data requirements of your company.
It determines the credibility of data for decision-making and how useful the data is for maximising operational efficiency.
The components of a data quality control process include the management of data quality requirements, rules for quality integrity requirements, and a plan for implementing and monitoring the data controls so you can get an accurate report and make continuous improvements.
A solid data quality control plan is designed to proactively uncover the data quality and integrity issues in a production environment.
It should yield useful information for solving data issues and should be applied to ensure a “continuously improving” data management environment.
In fact, there are more formal routes you can take in terms of quality control, including certifications that demonstrate your company’s ability to remain in compliance with regulations and verify that you have invested in the “know-how” to get the most out of your data.
Data governance certifications
For companies interested in pursuing a more formal route of demonstrating their commitment to EDM framework implementation these are a few professional certifications in data management available:
- DAMA Certified Data Management Professional (CDMP)
- Data Governance and Stewardship Professional (DGSP)
- edX Enterprise Data Management
- SAP Certified Application Associate – SAP Master Data Governance
Examples of EDM’s effectiveness
One example of how an EDM framework can be effective is demonstrated with an industrial company that had more than a dozen data sources that contained similar supplier information.
One source identified a supplier as Acme; another called it Acme, Inc.; and a third labeled it ACME Corp.
Traditional IT systems couldn’t truly understand their relationship with suppliers.
With proper EDM strategies, artificial intelligence tools were implemented to sift through such data chaos to assemble it properly.
The industrial company ultimately discovered an array of suppliers that were selling to multiple business units at the industrial company.
The discovery of this error yielded $75 million in savings once the errors were remedied.
Further evidence of a resourceful EDM strategy is demonstrated when we consider a global asset management company where the marketing and finance departments both produced monthly reports on television ad spending.
Marketing, interested in analysing advertising effectiveness, reported on spending after ads had aired.
Finance, focusing on cash flow, captured spending when invoices were paid.
The reports, therefore, contained different numbers.
The above two examples should demonstrate that your data is a company asset that needs to be treated with the same level of respect that you would any other piece of crucial business intelligence.
The proper implementation of the EDM framework components that we discussed above is your protocol for achieving your company’s data quality requirements.
The EDM framework, when properly implemented, allows your company to break away from data silos and ensures that you have immediate access to the crucial data that your company’s management team requires to make educated decisions.
Investing in a solid EDM framework yields data that is accurate, complete, and immediately available. And, that is what turns data into a strategic asset.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a data management framework?
A framework that enables your company to facilitate the management of its data as a strategic asset, thereby allowing your company to extract the maximum value from all the data that it works with and inventories; a framework that makes a company a data-driven organization.
What is the key element of enterprise data management?
It is the data governance element that is ultimately responsible for ensuring accountability for and ownership of data assets across an enterprise.
What is the data governance framework?
It is a system of principles that establishes accountability for information-related processes and maximizes the quality of your data throughout the complete lifecycle of the data at your company.




