5 minute read
Data management: How to be more agile in a decades-old practice
Data management is an old practice, and that's what makes it prone to sluggish performance. Here's how to change that with agile data management.
Table of contents
To manage your data effectively, your business needs to follow a lot of practices that aren’t exactly “agile.”
Storing data, processing, reporting with colleagues…
In the past, the mindset was always about “collecting data.” But to become truly agile, your mindset needs to shift from collecting data to creating value. Let’s explore ways to do that.
What is agile data management?
Agile data management is a methodology that helps you collect and analyse data more effectively, efficiently, and transparently to improve operational performance.
It enables you to get the most out of your business intelligence efforts and make better decisions faster.
It is based on the idea that there are no one-size-fits-all approaches to collecting and analysing data but rather a variety of tools and techniques that can be used in combination.
It also recognises that the best way to manage any organisation’s data is to tailor it to each organisation’s specific needs using relevant and up-to-date data.
With agile data management, you’re tracking every piece of data, whether in a record or not, and you’re ensuring that you can understand what’s happening with each piece.
An excellent example is an auction site where they collect information on each item to provide a more accurate price.
They also have a system that automatically updates this information based on new bids.
That’s where agile comes in.
The difference between agile and traditional data management
ADM helps companies make better decisions about storing, accessing, analysing, and sharing information.
In contrast, Traditional Data Management (TDM) refers to how companies traditionally hold, access, research, and share data.
TDM is based on a model where data is kept in silos and is only accessible to those who know the exact location of the data.
Unlike ADM, which handles massive data, traditional data management systems are not designed to handle the volume of data created by modern business processes.
These systems often require IT, teams to search for relevant data across databases and applications manually. As a result, many companies spend a lot of time searching for data instead of using it to drive business decisions.
Agile data management systems are designed to meet the challenges of large volumes of data. These systems help identify and access the right data at the right time.
4 benefits of agile data management
Here are some of the advantages of agile data management over traditional data management:
1. Better track record
According to the 2007 Project Success Survey, agile project teams have a success rate of 71.5%, compared to traditional teams’ success rate of 62.8%.
Agile has a higher success rate due to its enhanced emphasis on quality, return on investment (ROI), and capacity to meet the actual needs of business stakeholders.
2. Security
Agile data management solutions provide secure storage and access to sensitive data. Users can access the data they need without worrying about exposing confidential information.
3. Scalability
Agile data management platforms are scalable enough to handle the increasing volumes of data produced by modern business processes.
4. Cost and time savings
Agile data management tools reduce the cost associated with storing, accessing, analysing, and sharing data, helping you spend less time dealing with tedious tasks.
How to streamline your data management process
How often do you get overwhelmed with data management tasks? You might be wasting time and resources if you don’t have a clear plan for managing your data.
The amount of information generated from our daily lives has increased exponentially.
This means that we now create more data than ever before. In fact, in 2020, Techjury says every person makes an average of about 1.7 MB of data every second.
Data is everywhere. And with the rise of big data analytics, businesses can gain valuable insights into their customers and employees.
But how do they manage all this data?
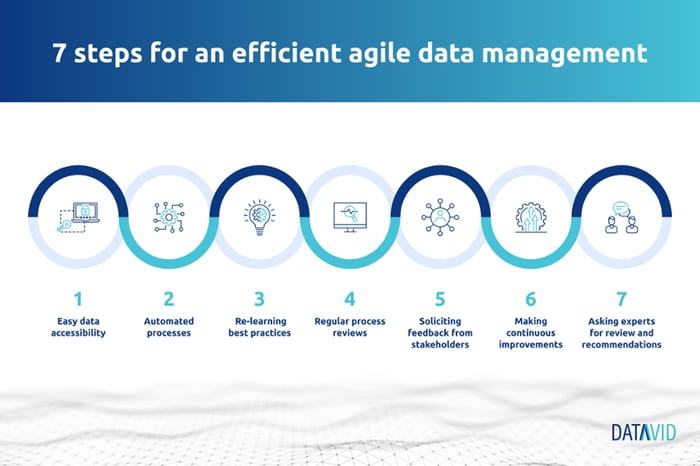
There are 3 best practices to streamline your data management:
Best practice #1: Make your data more accessible
If you don’t have access to your data, how do you know what to measure? How do you know if you are making progress?
Without data, you cannot make decisions.
Once you have identified your data sources, you can consider ways to improve its accessibility:
- Use a cloud-based service to share your files with others
- Back up your information regularly using a backup tool
- Share with colleagues and circulate around the firm
Data is meant to be used, and agile helps you achieve that.
Best practice #2: Make your process more efficient
Once you have access to your data and know where it comes from, you can start thinking about ways to make your process more efficient. There are many different data collection methods, each with advantages and disadvantages.
Best practice #3: Help your teams re-learn best practices
As you work to improve your data management process, you may find that some team members are resistant to change.
Remember, a data management plan is useless if no one knows.
Training sessions should be held regularly to ensure everyone understands their role in maintaining data integrity. These sessions should cover topics such as data storage, data classification, and data protection.
Agile data management: Which tools to use?
Many tools can help you with this, but because of the nature of agile, most will require some level of configuration or setup before you can use them effectively.
It means you’ll need to know about your organisation’s policies and those of your customers.
The idea behind agile data management is that your team should work in a flexible environment where things can be changed often and without major repercussions.
There needs to be a way for people to share information and make changes on the fly.
The most common way of doing this is using cloud-based storage systems such as Amazon’s S3 or Microsoft’s Azure File Storage Service.
These are ideal because they allow anyone on your team to access their files without having them stored locally on their computer or another server.
Other options are:
Option #1: PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL is a powerful open-source object-relational database management system (ORDBMS). It is a high-performance, multi-user, ACID-compliant, scalable, and freely available database management system.
Option #2: MongoDB
MongoDB is an open-source document-oriented database.
It is intended to handle large amounts of structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data.
MongoDB uses JSON documents to store data.
Option #3: Apache Derby
Apache Derby is an embedded relational database engine.
It is a lightweight, embeddable, transactional, and schemaless database. It is based on the Java programming language and runs on top of the Java Virtual Machine.
Option #4: HBase
HBase is a distributed, columnar, non-relational database similar to Google BigTable. It is built on HDFS and provides a RESTful API for querying and manipulating data.
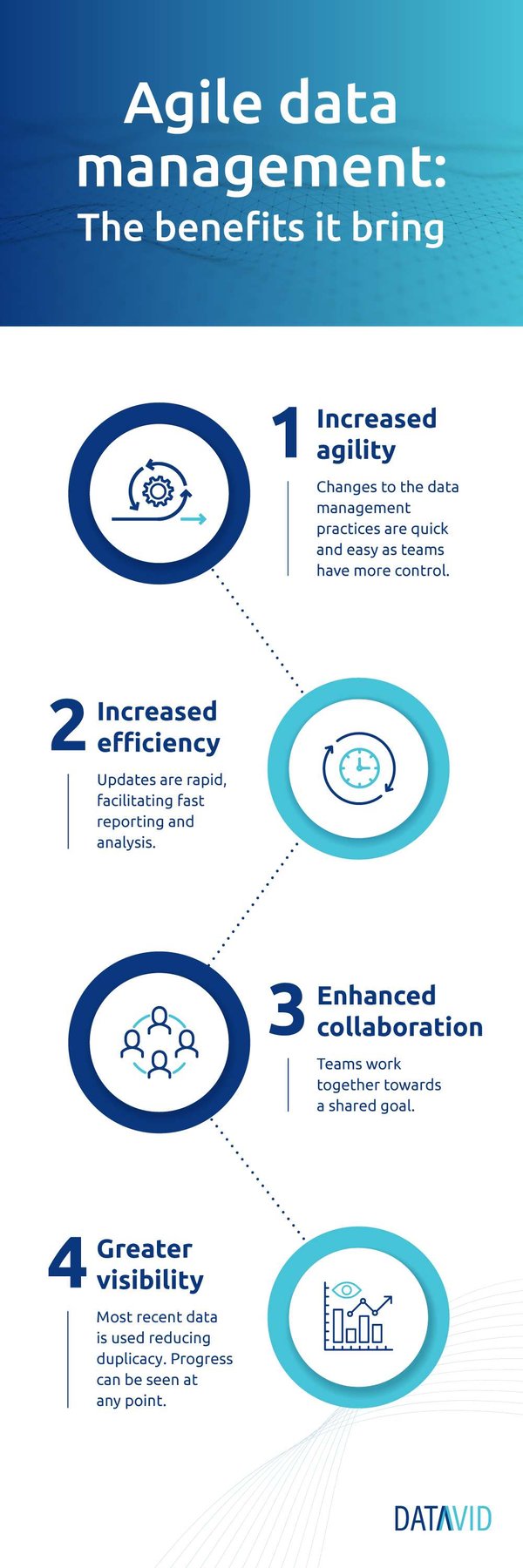
A brief overview of the agile data workflow
What was once a niche practice is now being embraced by IT organisations as part of their strategy for improving business agility and efficiency.
Anything “agile” refers to using iterative development processes to create value.
But how do you get started with agile data management?
Follow these 3 steps:
1. Development
The first step in agile data management involves creating a database that can be used in an agile environment.
The database should emphasise performance and scalability, allowing it to scale with the business as it grows.
2. Managing
During this phase, the organisation continues to develop its database using agile development methods, such as Test-Driven Development (TDD).
Agile development allows for frequent testing and iteration on changes to ensure they meet business requirements.
3. Deployment
Deployment involves moving from development into production environments where users will see results from testing and iteration on changes.
This phase includes deployment onto staging servers or production servers, depending on the stage of maturity.
Get started with agile data management
How often do you hear about data management issues? It’s always been a challenging topic for organisations, especially those wanting to scale their operations.
Data platforms like Datavid Rover can you help ease all of those issues.
It’s a powerful platform that combines data integration, entity extraction, and cognitive search, embracing the principles of agile within its architecture.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the use of agile affect data-driven decisions?
The use of agile helps organisations helps you focus on the value delivered, not just the data. This can help determine how much time and resources you need to devote to your data management efforts and how quickly you can make improvements for a swift decision-making process.
Can data governance be agile?
Yes! Data governance programs should be flexible and evolve as technology and as the organisation’s needs change. Effective data governance is agile; built around transparency, accountability, and traceability principles.
What Is MDM in Scrum?
Many companies use Scrum in Master Data Management (MDM) because it helps them deliver high-quality products faster. They can build records quickly because thanks to the process.