6 minute read
Exploring Robotic Process Automation (RPA): benefits and use cases
Repetitive business tasks cost enterprises time, accuracy, and resources. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can eliminate this drain by mimicking human actions across digital workflows. This article explores how.
Table of contents
Logistics operations, customer service, update machineries, data entry, translations, etc.
Think about how many repetitive processes your business does every day.
What if they could be automated?
A lot of time and resources would be saved.
This is the goal of Robotic Process Automation that we will explore in this article.
Let's find out what RPA is and what some of the uses and benefits of this technology are.
What is robotic process automation
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a software technology that simulates human activities while dealing with digital systems and software, regulated by business logic and structured inputs, with the goal to automate business operations.
The "robot" in robotic process automation refers to software robots that run on a physical or virtual machine.
Software robots can understand what's on a screen, complete the correct keystrokes, navigate systems, identify and extract data, and perform a wide range of defined actions faster and more consistently than people.
Using AI to enhance RPA
Modern RPA technologies incorporate artificial intelligence (AI), computer vision, and natural language processing, as well as some integration for centralised governance and administration, making it simpler to expand its use.
The ability of RPA to mimic how humans do computer-based processes has led to its popularity.
For example, one of the most basic RPA bots may be constructed simply by capturing a user's clicks and keystrokes while interacting with an app. When issues arise, a user may easily see how the bot connects with the app and discover the steps that need to be tweaked.
RPA, when combined with AI and machine learning, can extract more context from the content it is working with by reading text or handwriting with OCR, extracting entities such as names, invoice terms, or addresses using natural language processing, and extracting more context from images.
Types of RPA
There are three forms of robot process automation:
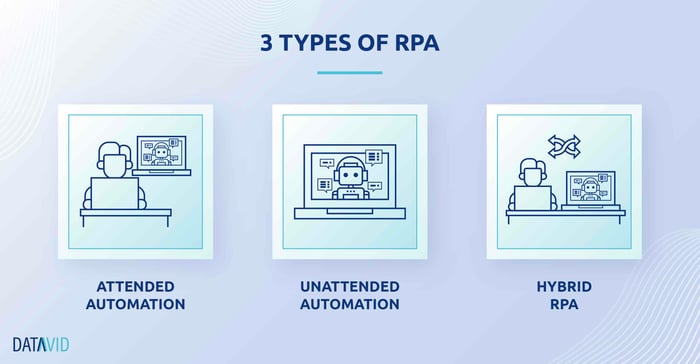
Attended automation
Attended automations are the ones that are executed under human supervision and, for this reason, are more suitable for smaller, fragmented tasks such as, for example, process an invoice.
Attended bots are often invoked by the user and can run on desktops, private servers, or in the cloud.
When a process cannot be fully automated, attended bots often work with humans to deliver elements of it. They can be compared to a human 'virtual assistant'.
Unattended automation
Unattended automations are those intended for complex and highly repetitive tasks, usually executed in batches and performed according to predefined rule.
Unattended bots may accomplish tasks without human intervention, and end-to-end automation, in which a bot can execute an entire process independently.
Unattended automation can be started in several ways, including data entry at a specific area, orchestrator activation, or logic in the process flow, such as an email and set intervals.
Hybrid RPA
Hybrid RPA combines attended and unattended RPA bots to provide automated activities. It enables process automation from start to finish.
RPA use cases
RPA is already creating new efficiencies and liberating employees from repetitive monotony across a wide range of businesses and procedures.
RPA has been used in areas as diverse as finance, compliance, legal, customer service, operations, and IT by businesses in industries ranging from financial services to healthcare to manufacturing to the public sector to retail and far beyond.
Here are some examples.
#1 RPA use case: Data extraction
RPA can be used for data extraction from PDFs, scanned papers, and almost any format possible using screen scraping, OCR, and simple pattern recognition algorithms.
This eliminates the need to manually extract and enter data.
#2 RPA use case: Invoice creation and delivery
RPA can be leveraged for data replication cases, like invoice creation and delivery.
The sales data in the CRM and accounting systems should be the same. To guarantee data integrity throughout systems, bots can update accounting records, prepare and transmit bills from the appropriate email accounts.
#3 RPA use case: Identifying security breaches
RPA bots can identify security breaches.
They automate security threat detection by managing privileged data, detecting malware in emails using specified keywords, doing cyber threat hunts.
#4 RPA use case: Automated testing
Testing tools that replicate user interactions developed into RPA technologies.
The tests can be embedded into the programme, but testing from the user's point of view is also essential.
Manual testing takes time, automated RPA testing is quick and can: Accelerate the corporate digital transformation and provide more dependable results.
For some cases, creative manual testing is necessary. Yet, no-code RPA systems are useful for routine tests that must be repeated.
#5 RPA use case: Inventory record updating
Inventory management generally entails reconciliation across different systems since organisations find it difficult to integrate all inventory management capabilities into a single system.
RPA bots can easily automate such intersystem reconciliation and communication.
#6 RPA use case: Data transfer from one system to another
Data backups and restorations for organisations can be entirely automated using RPA solutions by supplying them with the necessary credentials, source, and destination details for the entire job to be automated.
Monitoring the entire process may also be done by the RPA system, and a human task can be produced if human involvement is required.
Advantages of automating data transfers between systems saves administration hours, reduces the possibility of human errors, eliminates delays and bottlenecks caused by manual processes, streamlines the data transfer process and aids in resource conservation, and increases transparency and control through automated reporting.
#7 RPA use case: Updates to client profiles
Companies such as Facebook and others may experience lot of challenges as their client base is dispersed across all geographies, and frequent requests to back-end databases can also cause troubles in the overall application processing.
Those requests can then be handled by RPA-based solutions, which may process them as they come in to limit the burden on the back-end systems while also improving overall application speed.
Customer use case
A leading healthcare client of Datavid, who specialise in the manufacturing of medical equipment.
Challenges
They used a desktop application Endnote for reference management. They had to produce and publish the reports over the course of a year, and while doing so, they had to export the references from Endnote and import them into their own authoring tool.
All of this work was done manually each time by users.
Pain points
Some of the difficulties encountered were the following:
1. How to identify and click a specific button
There was the need for UI interactions to locate and click a button in the current view.
How is it possible to identify a button and only click that button in the entire view?
By some type of id parameter connected with that button. But, if there is no id parameter, the RPA tool will have a tough time identifying a certain element and performing any kind of action on it.
The same is true for text boxes. Workarounds are not the best options because they struggled to give accuracy, and they not always find the same element and perform the action, rather they try to perform the action on some element in the view at random.
2. How to maintain the host machine active
When automating UI interactions using Orchestrator triggers, the host machine should not go to sleep mode, have a screen saver enabled, or be locked.
If any of these occur, the UI interaction automation will be impeded and may stop in the middle if already started or may not be triggered at all.
It is not possible to lock the host machine, it should be placed in a safe area with only authorised access, as you may be dealing with sensitive data that should not be available to everyone at times.
Solution
Datavid team used RPA to automate this procedure in a proof-of-concept project.
Of all the solutions available on the market, I (and the team) chose to work with UiPath, designing the automation workflow in UiPath Studio and UiPath Orchestrator to provision, deploy, trigger, monitor, measure, and track the work of both attended and unattended robots.
The RPA tool in general is useful, especially for background processes (work), but UI interfaces can be hard and challenging. In that situation, there was a user interface interaction with a desktop programme.
RPA benefits
While RPA can perform numerous concurrent processes, scaling in an organisation might be problematic owing to regulatory updates or internal modifications.
According to a Forrester study , 52% of clients have difficulty growing their RPA programme.
But, RPA has several benefits, including:
- Less coding
RPA does not always need to be configured by a developer; drag-and-drop functionalities in user interfaces make it easier to onboard non-technical workers.
- Improved accuracy and compliance
RPA robots may be programmed to follow precise workflows and regulations, this way you can eliminate human error, especially in work that needs precision and compliance, such as regulatory requirements. RPA may also offer an audit trail, making it easier to track progress and rectify difficulties.
- Existing systems remain in place
Since bots’ function on the presentation layer of current applications, robotic process automation software has little impact on underlying systems. As a result, you can use bots even if you don't have an application programming interface (API) or the resources to build complex integrations.
5 RPA tools on the market
There are several firms with RPA products on the market today; a few well-known and popular ones are:
1) UiPath Business Automation Platform by UiPath
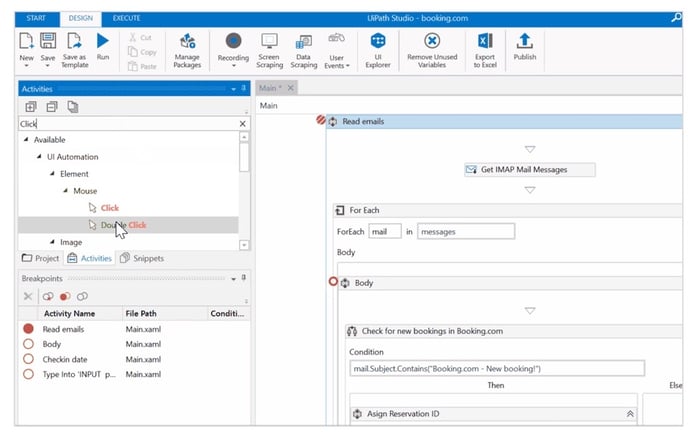
Source: g2.com
Some UiPath Business Automation Platform key benefits and features it offers are:
- Low-code development
- UI and API automation
- Process orchestration
- Intelligent document processing
- Integrated NLP and AI/ML
2) Automation 360 by Automation Anywhere
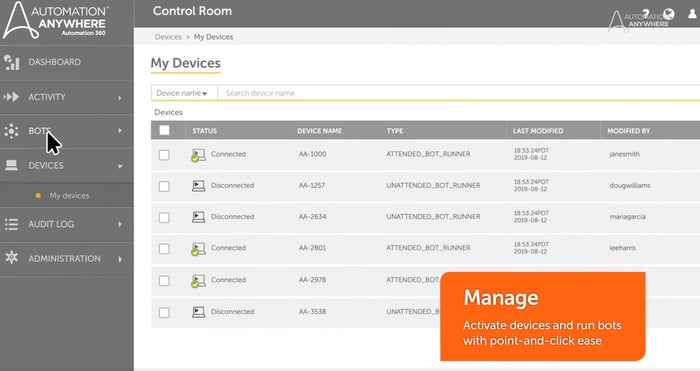
Source: Automation Anywhere
Some Automation 360 key benefits and features it offers are:
- Discoverability of every process
- Digitisation of all your data
- Automation of repetitive work
- Adaption and optimisation of operations
3) Blue Prism Intelligent Automation Platform by SS&C Blue Prism
Source: Software advice
Some Blue Prism Intelligent Automation Platform key benefits and features it offers are:
- Exponential growth
- Security and auditability
- Customer experience
- Speed-to-value
4) Conversational RPA by AutomationEdge
Source: AutomationEdge
Some Conversational RPA key benefits and features it offers are:
- Understanding of context and language nuances
- Automate business (e.g. email contact center)
- Notifications on important event or updates
- Assistance for efficient human agents
- No code visual AI dialog flow studio
- No code visual RPA and API workflow studio
5) IBM Robotic Process Automation by IBM
Source: IBM
Some IBM Robotic Process Automation key benefits and features it offers are:
- A quick start
- Operationalisation of AI
- Faster ROI
- A focus on business and IT
- Full-featured RPA
- Reduction of cost of ownership

Source: Gartner
Frequently Asked Questions
What is RPA?
RPA stands for Robotic Process Automation, which uses software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks in business processes.
Is RPA really Al?
RPA (Robotic Process Automation) is not considered true artificial intelligence (AI). While RPA involves automation of repetitive tasks using software robots, it does not possess advanced cognitive capabilities or learning abilities associated with AI.
What is the most widely used RPA tool?
UiPath is currently one of the most widely used RPA (Robotic Process Automation) tools in the market.